Hello, aspiring investors! I’m your friendly financial educator here at MarketsFN, dedicated to breaking down complex finance concepts into bite-sized, easy-to-understand pieces. Today’s word of the day is “convertible bonds.” If you’re new to investing, you might think bonds are just boring loans to companies or governments, and stocks are the exciting shares that can make you rich (or broke). But what if I told you there’s a financial instrument that combines the best of both worlds? That’s right—convertible bonds are like the Swiss Army knife of investments, offering stability with a dash of growth potential. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what they are, how they work, their pros and cons, and some real-world examples. By the end, you’ll feel confident enough to spot them in the wild (or at least explain them at your next dinner party). Let’s get started!
What Exactly Are Convertible Bonds?
At their core, convertible bonds (often just called “convertibles”) are a type of corporate bond that gives the holder the option to convert them into a predetermined number of shares of the issuing company’s common stock. Think of it as a bond with a built-in “upgrade” feature. Unlike regular bonds, which simply pay you interest (called coupons) and return your principal at maturity, convertibles add an equity twist. This hybrid nature makes them appealing in volatile markets, where investors want income but also the chance to benefit from a company’s stock price rising.
To put it simply: Imagine lending money to a friend (the company) with interest, but with the option to turn that loan into ownership in their booming business if things go well. That’s the essence. Convertible bonds are issued by companies, typically those in growth sectors like technology or biotech, to raise capital without immediately diluting their stock. They’re fixed-income securities, meaning they have a set interest rate and maturity date, but the conversion option adds flexibility.
Why do they exist? Companies use them to borrow money at lower interest rates than traditional bonds because the conversion feature is like a sweetener for investors. For beginners, this means convertibles can be a gentler entry into the stock market— you get bond-like safety nets while dipping your toes into equity upside.
How Do Convertible Bonds Work? A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Let’s break this down like we’re assembling a simple puzzle. Convertible bonds start life just like any other bond. When a company issues one, you (the investor) buy it at face value, say $1,000. The company promises to pay you periodic interest, perhaps 3-5% annually, and repay the $1,000 at maturity, which could be 5-10 years later.
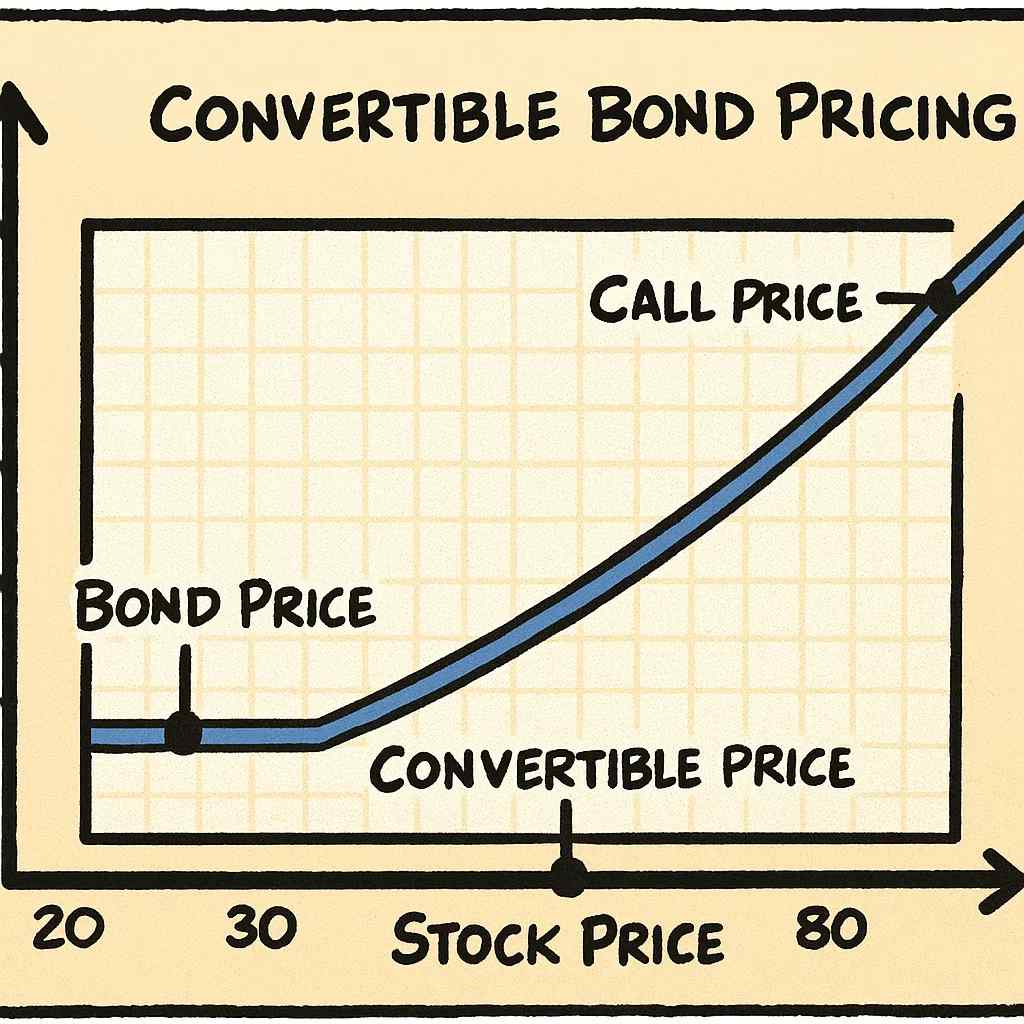
But here’s the magic: The bond comes with a conversion ratio, which tells you how many shares you can get if you convert. For example, a conversion ratio of 20 means you can swap your $1,000 bond for 20 shares of the company’s stock. The conversion price is essentially the face value divided by the ratio—in this case, $50 per share ($1,000 / 20).
Conversion isn’t mandatory; it’s your choice. You might convert if the stock price rises above the conversion price (say, to $60), because those 20 shares would then be worth $1,200—more than your bond’s value. If the stock tanks to $30, you keep the bond for its interest and principal, providing a “floor” of protection.
There are a few key triggers:
- Voluntary Conversion: You decide when to convert, usually after a certain period.
- Call Feature: The company might “call” the bond back early if the stock price surges, forcing you to convert or redeem at a premium.
- Put Feature: In some cases, you can “put” the bond back to the company early.
Pricing is influenced by the bond’s value (interest rates, credit risk) and the embedded option (stock volatility). When the stock is low, the convertible acts like a bond; when high, like stock. This asymmetry is why they’re popular in uncertain times.
Key Terms Every Beginner Should Know
To sound like a pro, let’s cover some jargon:
- Par Value/Face Value: The amount you lend and get back at maturity, e.g., $1,000.
- Coupon Rate: The interest paid, often lower than straight bonds (2-4%) due to the conversion perk.
- Maturity Date: When the bond ends—convert or get paid.
- Conversion Premium: The extra amount you’d pay for shares via conversion vs. market price. A 20% premium means the conversion price is 20% above current stock.
- Bond Floor: The minimum value based on straight bond worth, protecting against stock drops.
- Parity: When bond value equals the stock value post-conversion.
Understanding these helps you evaluate if a convertible is a good fit.
Advantages for Investors: Why You Might Love Them
For beginners, convertibles offer a balanced risk-reward profile. Here’s why:
- Income with Upside: You get steady interest payments, like a bond, but if the company thrives, convert for stock gains. It’s like having a safety net while reaching for higher returns.
- Downside Protection: If the stock flops, you still have the bond’s principal and interest—better than pure stock losses.
- Diversification: They blend debt and equity, reducing portfolio volatility. In 2025’s market, with interest rates fluctuating, convertibles have yielded attractive returns amid equity booms.
- Lower Volatility: Studies show convertibles often have less price swing than stocks, making them suitable for conservative investors exploring growth.
Imagine you’re risk-averse but want tech exposure. A convertible from a startup lets you earn interest while waiting for potential IPO hype.
Advantages for Issuers: Why Companies Issue Them
From the company’s side, convertibles are a smart financing tool:
- Cheaper Borrowing: Lower coupon rates (1-2% less than regular bonds) because investors value the conversion option.
- Delayed Dilution: No immediate share issuance; dilution only if converted, often at a premium price.
- Attract Investors: Appeals to those seeking hybrids, especially in growth phases. In 2025, issuance hit $80 billion globally in H1, up 17.6%, as firms like tech giants tapped strong markets.
- Flexibility in Volatile Times: Companies can call bonds if stocks rise, managing debt efficiently.
For example, startups use them to fund R&D without high interest burdens.
The Risks: No Investment Is Perfect
Convertibles aren’t risk-free. Beginners, beware:
- Interest Rate Risk: Like bonds, prices fall if rates rise.
- Credit Risk: If the company defaults, you lose principal—check ratings!
- Conversion Risk: If stock never rises, you’re stuck with low-yield bond.
- Call Risk: Company might force early conversion, capping upside.
- Liquidity Risk: Some aren’t heavily traded, hard to sell quickly.
In 2025’s environment, with potential rate cuts, convertibles shine, but economic slowdowns could hurt.
Real-World Examples: Bringing It to Life
Let’s look at examples to solidify this.
Historical Gem: Tesla’s Convertibles
Tesla issued convertibles in 2014 ($2.3 billion at 0.25% interest, convertible at $359.87/share). As stock soared past $1,000 (pre-split), holders converted for massive gains. Beginners note: Early investors got bond safety during volatility, then equity windfall.
2025 Surge: Tech and Pharma Boom
In 2025, convertible issuance boomed. For instance, a hypothetical biotech firm like “BioInnovate” issues $500 million at 2% coupon, convertible at $50/share (current stock $40). If a breakthrough drug succeeds, stock hits $70—converters profit. Real trends: Companies in AI and renewables raised billions, with 17 deals over $1 billion in H1.
Another Case: Airline Recovery Bonds
Post-pandemic, airlines like Delta issued convertibles in 2021 (extended relevance in 2025). $1.25 billion at 1.625%, convertible at $74.46. As travel rebounded, conversions yielded equity upside while providing debt during downturns.
These show convertibles thrive in growth stories.
How to Invest in Convertible Bonds as a Beginner
Ready to dip in? Start small:
- Research: Use sites like Fidelity or Vanguard for funds (e.g., Vanguard Convertible Securities Fund).
- ETFs/Mutual Funds: Easier than individual bonds—try CALF or ICVT ETFs.
- Brokerage Accounts: Buy via platforms like Robinhood or E*TRADE.
- Diversify: Don’t put all eggs here; aim for 5-10% of portfolio.
Monitor via Bloomberg or Yahoo Finance. In 2025, with equity markets strong, convertibles offer yields and growth.
Wrapping Up: Are Convertible Bonds Right for You?
Convertible bonds are a fantastic tool for beginners bridging bonds and stocks—offering income, protection, and upside. They’re especially hot in 2025 amid market optimism and innovation booms. But remember, they’re not for everyone; assess your risk tolerance.
Disclaimer
The content on MarketsFN.com is provided for educational and informational purposes only. It does not constitute financial advice, investment recommendations, or trading guidance. All investments involve risks, and past performance does not guarantee future results. You are solely responsible for your investment decisions and should conduct independent research and consult a qualified financial advisor before acting. MarketsFN.com and its authors are not liable for any losses or damages arising from your use of this information.